
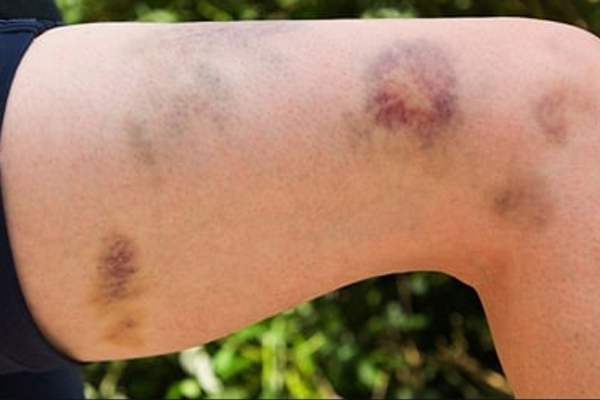
The macular rash begins as erythematous and then becomes purpuric and raised.

If not diagnosed and treated swiftly complications can include:¹ In addition, corticosteroids (e.g: intravenous dexamethasone) is given in those over 3 months old to reduce neurological complications. Intravenous ceftriaxone in patients over 3 months old.Intravenous cefotaxime and amoxicillin in patients under 3 months.Local microbiology guidelines should be followed. If the patient is seen in primary care intramuscular benzylpenicillin can be given whilst awaiting transfer to hospital. This is an emergency and the patient will need immediate transfer to hospital.Īntibiotics need to be given immediately. Lumbar puncture: the definitive investigation to diagnose meningococcal meningitis.Pharyngeal swab: to screen for the presence of Neisseria meningitides in the pharynx.
#Platelet disorders pinpoint rash skin#
Hypovolaemic shock: low blood pressure, high heart rate, capillary refill time >2s, the skin may look mottled.Brudzinski’s sign (knees and hips flex on bending the head forward).Kernig’s sign (pain and resistance on passive knee extension with hips fully flexed).Important findings on examination include: If meningitis/meningococcal sepsis is suspected, patients should undergo a thorough examination and the skin should be assessed for any rashes. Typical symptoms of meningococcal sepsis include: A second smaller peak has been recognised in 14-19-year-olds. Meningococcal meningitis is most common in children under 5 years of age. Meningococcal sepsis is a complication of meningitis which occurs when the infection moves beyond the central nervous system into the blood. Meningococcal meningitis is a central nervous system infection commonly caused by Neisseria meningitides, a gram-negative diplococcus and commensal of the nasopharynx. You might also be interested in our medical flashcard collection which contains over 2000 flashcards that cover key medical topics.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
